研究背景・先行研究
通常,ロボットをはじめとする機械システムや生体システム,交通システムなどの動的システムを制御しようとするとき,まずその対象を運動方程式などの微分方程式もしくは差分方程式で表現し,数式に現れるパラメータをシステム同定により同定したあと,それに基づいて制御則を設計するという手順を取る.ただし実際のシステムを数式で完全に表現することは難しく,またシステム同定により正しくパラメータを推定できるとは限らないため,得られるシステムは常に不確かさを含んでいる.
適応制御とは,フィードバックゲインを適応的に調整することで,不確かさを持つシステムの安定化や目標値への追従を達成する制御手法である.ロボットマニピュレータの制御[1-4]や投薬スケジュールの設計[5-8],電力系統の制御[9-11]に応用されている.
不確かさを持つシステムに対する適応制御手法は,連続時間システムに対する適応制御手法のみならず,離散時間システムに対する適応制御手法も先行研究において多く提案されている.
文献[12,13]では,離散時間LTIシステムに対して逐次最小二乗法を基にしたアルゴリズムを用いてシステムの出力の目標値への追従を実現している.また文献[14-17]ではマッチング条件を満たすような多入力の非線形システムに対して適応制御則を提案し,Lyapunov関数を用いて閉ループシステムの平衡点がLyapunov安定であること,プラントの状態変数が漸近的に0に収束することを保証している.文献[18]ではマッチング条件を満たすような非線形の離散時間非負システムに対する適応制御則を提案し,閉ループシステムの安定性をLyapunov関数を用いて保証している.また文献[19]ではReceptive Field Weighted Regressionという局所モデルの重ね合わせにより非線形関数を近似する手法を用いて,未知項があるような非線形システムに対し閉ループシステムを安定化させるような適応制御則を提案している.
文献[20-24]では,バックステッピングという手法を用いて離散時間システムを適応的に制御する手法が数多く提案されている.バックステッピングによる適応制御手法は状態方程式にStrict Feedback Formと呼ばれる特定の構造をもつシステムを対象としている.文献[25-28]では,不確かさを持つ離散時間非線形システムに対して出力フィードバックを用いてシステムの出力を目標値に追従させる適応制御手法を提案しており,閉ループシステムの解軌道がSemiglobally Uniformly Ultimately Boundedであることが保証されている.文献[28]では,未知パラメータが線形の形で状態方程式に含まれているような単入力の離散時間非線形システムに対する適応制御手法を提案している.提案された適応制御アルゴリズムによりシステムの状態変数が目標値に追従することと,状態方程式に含まれる未知パラメータの推定値がその真値に収束することが保証されている.また文献[29]では、離散時間の非線形MIMOシステムに対してバックステッピングを用いた適応制御手法を提案している.提案されている制御手法により,システムの出力が目標値に追従することが示されている.この文献では非線形の関数を推定するために高次元のニューラルネットワークを用いており,そのニューラルネットワークの重みの更新にはExtended Kalman Filterを応用した更新則を用いている.文献[20]では,ダイナミクスが未知であり,かつ状態方程式が入力に関して非アファインであるような多入力多出力のの非線形システムに対する適応制御手法を提案している.さらに,ここで対象とするシステムの入力に関する未知の非線形項にはサチュレーションと不感帯が存在するとしている.提案されている制御則は閉ループシステムの解が半大域的に一様に終局有界であることを保証している.
また,強化学習という機械学習分野で用いられてきた学習手法を応用した不確かなシステムに対する適応制御手法が数多く提案されている.文献[30]では,アクチュエーターの飽和制約を備えた離散時間非線形システムに対する適応学習制御手法を提案している.この文献においては,2つのニューラルネットワークを用いてシステムに含まれる未知の非線形関数と,強化学習における効用関数に相当する評価関数を近似し,評価関数が最小となるような制御入力を設計している.リアプノフ関数を用いた解析により,提案された制御手法によって状態変数が目標値に追従することとニューラルネットワークの重みが有界となることが保証されている.また,文献[31-36]では,強化学習という教師なし学習手法を応用したPolicy Iterationという手法を用いて,ダイナミクスが未知であるような線形動的システムの適応制御手法を提案している.Policy Iterationとは強化学習の手法の1つであり,文献[31-36]ではリアプノフ関数の値を計算し,それに対応する最適フィードバックゲインを求めるというステップを繰り返すことにより最適なフィードバックゲインを計算していくアルゴリズムを用いている.フィードバックゲインの初期値(0ステップ目のフィードバックゲインの値)として閉ループシステムを安定化させるようなものを選んだならば,このアルゴリズムにより最適フィードバックゲインが計算できることが示されている.文献[32]ではシステムのA行列が未知であり,B行列が既知であるような連続時間LTIシステムに対して,文献[33]ではシステムパラメータが未知であるような離散時間LTIシステムに対して適応制御学習手法を提案している.文献[34]では出力フィードバックを用いたときのPolicy Iterationによる適応学習制御手法を提案している.文献[35]ではシステムパラメータが未知であるような離散時間線形システムに対して,LMIを用いてH∞コントローラを設計する手法を提案している.文献[36]では,不確かな非線形システムに対して最適制御入力を逐次的に計算するPolicy Iterationを基にしたアルゴリズムを提案している.
また近年では,不確かなシステムに対する制御器設計の手法として,データ駆動型制御器設計と呼ばれる制御器設計手法が注目を集めている.データ駆動型制御器設計においては,現代制御論等に基づくモデルベースの制御器設計とは異なりシステムの入出力情報を直接利用して制御器を設計する.つまりシステムのダイナミクスのモデルを陽に利用せず制御器設計を行うため,システム同定を行う必要がない,システム同定によりモデル化できないダイナミクスの影響を考慮する必要がないなどの利点がある[37].データ駆動型制御器設計法は,システムの入出力時系列の訓練データをあらかじめ取得しておき,その訓練データを用いて制御器を設計する手法[38-40]と,逐次的にシステムの入出力データを取得しながら制御器の設計を行う適応制御的な設計手法が存在する.適応制御的なデータ駆動型制御手法としては,Model Free Adaptive Control[41-43]やUnfalsified Control[44-48],Lazy Learningを用いた制御手法[49]等が挙げられる.しかしデータ駆動型制御器設計法の問題点として,設計された制御器が安定性(内部安定性等)などの重要な性質を保証できていない設計手法が多くあることが挙げられる.
本研究の目的
本研究では,マッチング条件[50]と呼ばれる動的システムの持つ不確かさに関する条件に着目する.ただしマッチング条件を満たすシステムとは,システムに含まれる不確かさを制御入力によって打ち消すことができるようなシステムである.システムの持つ不確かさを制御入力で打ち消すことができるかどうかは,不確かさの構造と入力行列の構造に依存しており,数学的に言えば,不確かさの列空間が入力行列の張る空間に含まれていれば,その不確かさは制御入力により打ち消すことができる.先行研究において提案されているマッチング条件を仮定しない離散時間システムに対する適応制御手法においては,システムのダイナミクスを表す差分方程式にStrict Feedback Form等の特別な構造が仮定されていること[22,25,27-29],もしくはシステムの状態変数が持続励振条件を満たしていること[30-36]が閉ループシステムの安定化を保証するために必要である.つまり,Strict Feedback Form等の差分方程式の特別な構造に関する条件や,システムの状態変数に関する持続励振条件,およびマッチング条件が仮定されていないような離散時間動的システムに対する,閉ループシステムの安定化を保証する適応制御手法は提案されていない.
また,文献[14-17]で提案された適応制御手法はStrict Feedback Form等の差分方程式の特別な構造に関する条件や,システムの状態変数に関する持続励振条件を必要としないが,システムがマッチング条件を満たしていることを仮定している.つまりマッチング条件を満たすシステムに対しては閉ループシステムの平衡点の安定性を保証するが,マッチング条件を満たさないシステムに対しては閉ループシステムの平衡点が安定となることを保証することができない.
そこで本研究では,文献[14,15]で提案された適応制御手法を改良し,Strict Feedback Form等の差分方程式の特別な構造に関する条件や,システムの状態変数に関する持続励振条件,およびマッチング条件が満たされていることが仮定されていないシステムを安定化する新しい適応制御手法を提案することを目的とする.
提案する適応制御手法
本研究では,マッチング条件が仮定されていない離散時間動的システムに対して,制御入力のフィードバックゲインだけでなくフィードバックゲインの更新式に含まれるパラメータも逐次的に調整するような適応学習制御手法を提案する.システムの持つ不確かさの非線形性に対してはニューラルネットワークを用いた近似を行い,そのゲインも逐次的に調整する.
そして,閉ループシステムに正不変集合が存在すること,閉ループシステムの平衡解がLyapunov安定であることを文献[51]に基づきLyapunov関数を用いて示す.また,閉ループシステムの平衡解がLyapunov安定となるとき、プラントの状態変数が漸近的に0に収束することを部分安定性の理論[52]により示す.数値シミュレーションを図1--図3に示す.
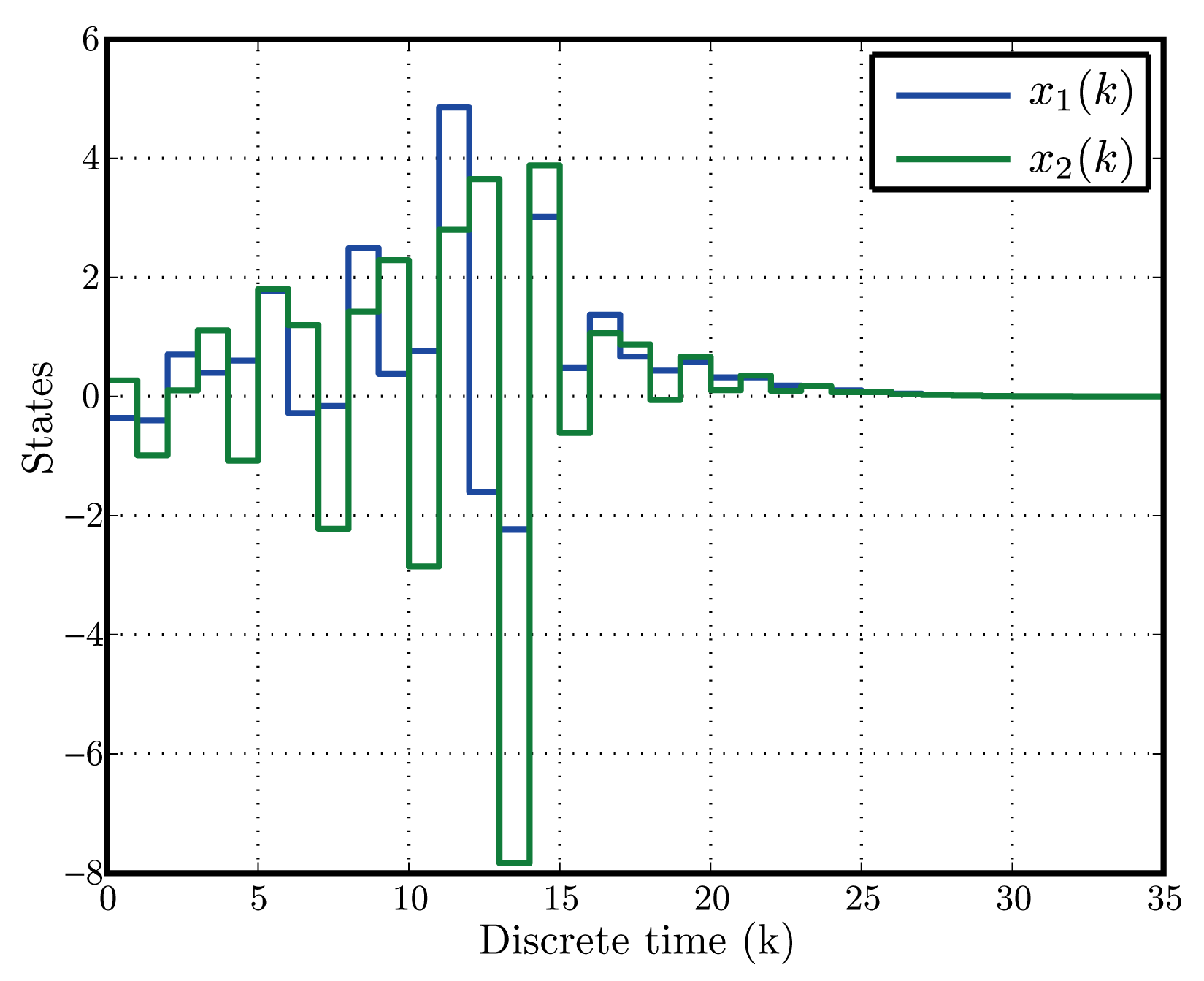 |
| 図1: state trajectories |
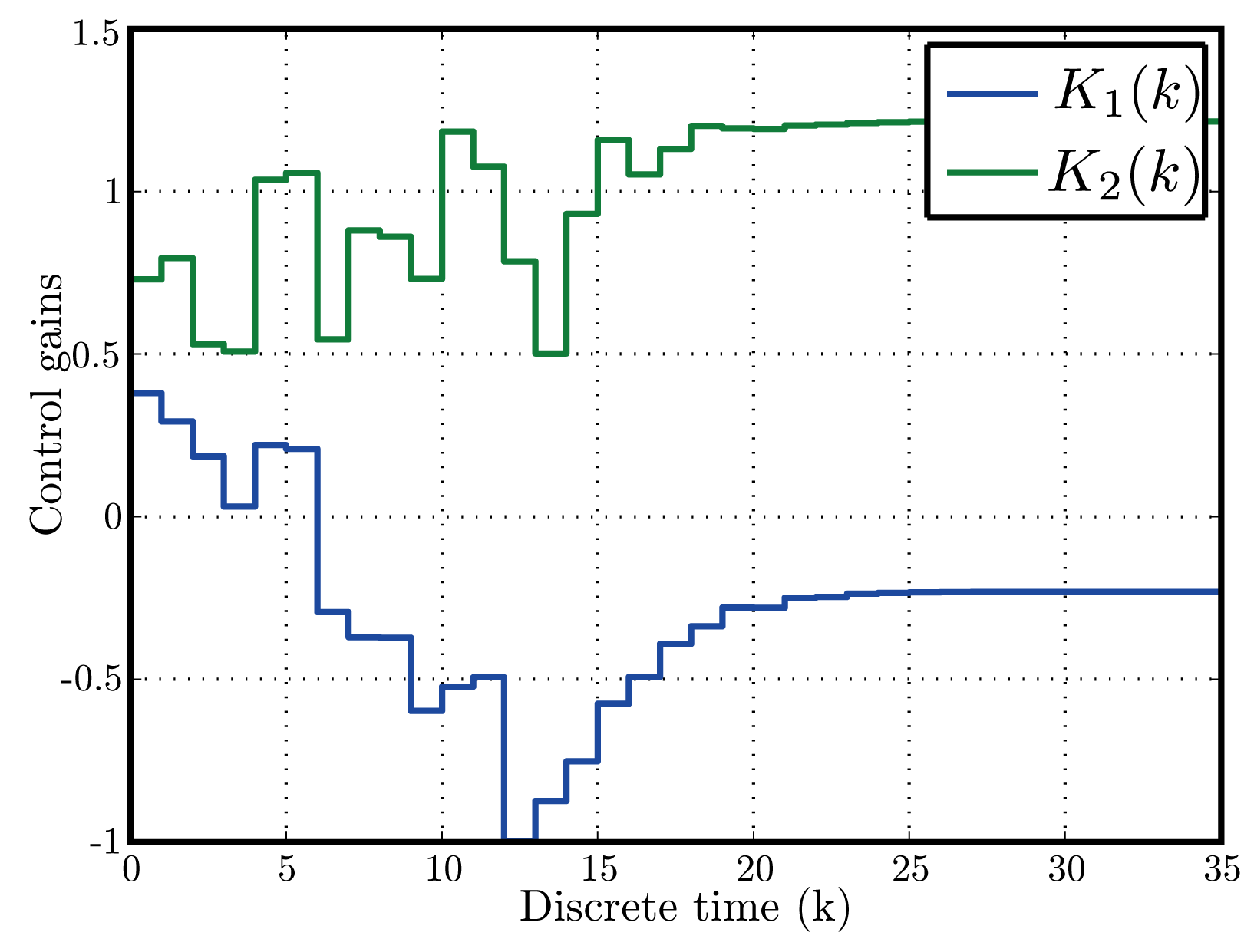 |
| 図2: Histories of adaptive control gains |
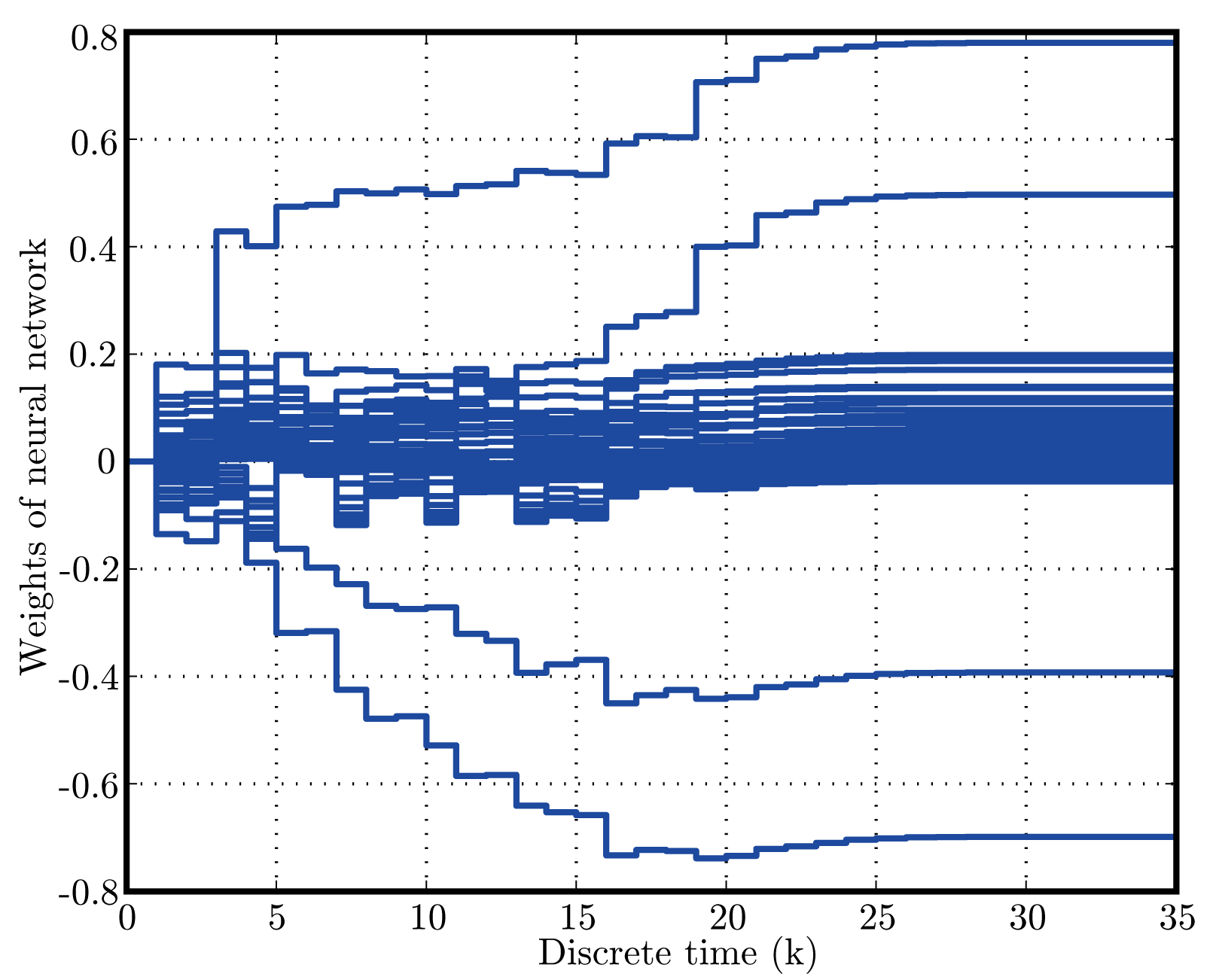 |
| 図3: Histories of neural network weighting functions |
今後の方針
本研究で提案した適応学習制御手法は,プラントの状態変数に関する局所的な漸近安定性しか示せていない.そこで今後の方針として,プラントの状態変数に関する大域的な漸近安定性を保証するような制御手法を提案することが挙げられる.また,マッチング条件を仮定しない離散時間非負システム[53]に対する適応制御則を提案することも今後の方針として挙げられる.
参考文献
[1] R. Lozano and B. Brogliato, "Adaptive control of robot manipulators with flexible joints," IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 174-181, 1992.
[2] Kye Y. Lim and M. Eslami, "Robust adaptive controller designs for robot manipulator systems," IEEE Journal of Robotics and Automation, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 54-66, 1987.
[3] J.-J.E. Slotine and Li Weiping, "Adaptive manipulator control: A case study," IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 33, no. 11, pp. 995-1003, 1988.
[4] V. Feliu, K.S. Rattan and H.B. Brown Jr., "Adaptive control of a single-link flexible manipulator," IEEE Control Systems Magazine, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 29-33, 1990.
[5] B. Schoeberl, U.B. Nielsen and R. Paxson, "Model-based design approaches in drug discovery: A parallel to traditional engineering approaches," IBM Journal of Research and Development, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 645-651, 2006.
[6] Gregory I. Voss, Peter G. Katona and H.J. Chizeck, "Adaptive Multivarable Drug Delivery: Control of Artenal Pressure and Cardiac Output in Anesthetized Dogs," IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 34, no. 8, pp. 617-623, 1987.
[7] Gregory W. Neat, H. Kaufman and Rob J. Roy, "Expert adaptive control for drug delivery systems," IEEE Control Systems Magazine, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 20-24, 1989.
[8] M.M. Polycarpou and J.Y. Conway, "Indirect adaptive nonlinear control of drug delivery systems," IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 43, no. 6, pp. 849-856, 1998.
[9] Rui Yan, ZhaoYang Dong, T.K. Saha and Rajat Majumder, "A power system nonlinear adaptive decentralized controller design," Automatica, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 330-336, 2010.
[10] Yong Wan, Jun Zhao and Georgi M. Dimirovski, "Nonlinear adaptive control for multi-machine power systems with boiler-turbine-generator unit," International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems, vol. , no. , pp. , 2014.
[11] Diarmaid J. Hogan, Fran Gonzalez-Espin, John G. Hayes, Gordon Lightbody and Michael G. Egan, "Adaptive resonant current-control for active power filtering within a microgrid," Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), pp. 3468-3475, 2014.
[12] G.Goodwin, P.J.Ramadge and P.E.Caines, "Discrete-time multivariable adaptive control," IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 449-456, 1980.
[13] E.-W. Bai and Shankar S. Sastry, "Discrete-time adaptive control utilizing prior information," IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 31, no. 8, pp. 779-782, 1986.
[14] Tomohisa Hayakawa, Wassim M. Haddad and Alexander Leonessa, "A Lyapunov-based adaptive control framework for discrete-time non-linear systems with exogenous disturbances," International Journal of Control, vol. 77, no. 3, pp. 250-263, 2004.
[15] T.Hayakawa, M.M.Haddad and N.Hovakimyan, "Neural Network Adaptive Control for a Class of Nonlinear Uncertain Dynamical Systems With Asymptotic Stability Guarantees," IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 80-89, 2008.
[16] K. Y. Volyanskyy and W. M. Haddad, "A Q-Modification Neuroadaptive Control Architecture for Discrete-Time Systems," IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, vol. 21, no. 9, pp. 1507-1511, 2010.
[17] S.H.-S. Fu and Chi-Cheng Cheng, "Direct adaptive control designs for nonlinear discrete-time systems with matched uncertainties," Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics, pp. 881-886, 2005.
[18] Wassim M. Haddad, VijaySekhar Chellaboina, Qing Hui and Tomohisa Hayakawa, "Neural Network Adaptive Control for Discrete-Time Nonlinear Nonnegative Dynamical Systems," Advances in Difference Equations, vol. 2008, no. 1, pp. , 2008.
[19] Jun Nakanishi and Jay A. Farrell and Stefan Schaal, "Composite adaptive control with locally weighted statistical learning," Neural Networks, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 71-90, 2005.
[20] Mou Chen, S.S. Ge and B. Voon Ee How, "Robust Adaptive Neural Network Control for a Class of Uncertain MIMO Nonlinear Systems With Input Nonlinearities," IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 796-812, 2010.
[21] Youan Zhang, Yun-an Hu, Zhao-Qing Song and Ping-Yuan Cui, "CMAC neural networks-based adaptive control for discrete-time nonlinear systems with unmatched uncertainties by backstepping," Proceedings of the 3rd World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, vol. , no. , pp. 3200-3204, 2000.
[22] S.S. Ge, G.Y. Li and T.H. Lee, "Adaptive NN control for a class of strict-feedback discrete-time nonlinear systems," Automatica, vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 807-819, 2003.
[23] S. S. Ge, Jin Zhang and Tong Heng Lee, "Adaptive neural network control for a class of {MIMO} nonlinear systems with disturbances in discrete-time," IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 1630-1645, 2004.
[24] Shuzhi Sam Ge, Chenguang Yang, Shi-Lu Dai, Zongxia Jiao and Tong Heng Lee, "Robust adaptive control of a class of nonlinear strict-feedback discrete-time systems with exact output tracking," Automatica, vol. 45, no. 11, pp. 2537-2545, 2009.
[25] Shi-Lu Dai, Chenguang Yang, S.S.Ge and Tong-Heng Lee, "Robust adaptive output feedback control of a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems perturbed by nonlinear uncertainties," Proceedings of the 48th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control 2009 held jointly with the 2009 28th Chinese Control Conference, pp. 7686-7691, 2009.
[26] Chenguang Yang, Shuzhi Sam Ge and Tong Heng Lee, "Output feedback adaptive control of a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems with unknown control directions," Automatica, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 270-276, 2009.
[27] Chenguang Yang, Yanan Li, Shuzhi Sam Ge and Tong Heng Lee, "Adaptive predictive control of a class of discrete-time MIMO nonlinear systems with uncertain couplings," American Control Conference (ACC), 2010, pp. 2428-2433, 2010.
[28] Yaprak Yalçin and Alessandro Astolfi, "Immersion and invariance adaptive control for discrete time systems in strict feedback form," Systems & Control Letters, vol. 61, no. 12, pp. 1132-1137, 2012.
[29] Alma Y Alanis, Edgar N Sanchez and Alexander G Loukianov, "Discrete-time adaptive backstepping nonlinear control via high-order neural networks," IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 1185-1195, 2007.
[30] Pingan He and Sarangapani Jagannathan, "Reinforcement learning neural-network-based controller for nonlinear discrete-time systems with input constraints," IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B: Cybernetics, vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 425-436, 2007.
[31] S. Bhasin, R. Kamalapurkar, M. Johnson, K.G. Vamvoudakis, F.L. Lewis and W.E. Dixon, "A novel actor-critic-identifier architecture for approximate optimal control of uncertain nonlinear systems," Automatica, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 82-92, 2013.
[32] D. Vrabie, O. Pastravanu, M. Abu-Khalaf and F.L. Lewis, "Adaptive optimal control for continuous-time linear systems based on policy iteration," Automatica, vol. 45, no. 2, pp. 477-484, 2009.
[33] Asma Al-Tamimi, Frank L. Lewis and Murad Abu-Khalaf, "Model-free Q-learning designs for linear discrete-time zero-sum games with application to H-infinity control," Automatica, vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 473-481, 2007.
[34] F.L. Lewis and K.G. Vamvoudakis, "Optimal adaptive control for unknown systems using output feedback by reinforcement learning methods," 2010 8th IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA), pp. 2138-2145, 2010.
[35] J.-H. Kim and F.L. Lewis, "Model-free control design for unknown linear discrete-time systems via Q-learning with LMI," Automatica, vol. 46, no. 8, pp. 1320-1326, 2010.
[36] Draguna Vrabie and Frank Lewis, "Neural network approach to continuous-time direct adaptive optimal control for partially unknown nonlinear systems," Neural Networks, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 237-246, 2009.
[37] Zhong-Sheng Hou and Zhuo Wang, "From model-based control to data-driven control: Survey, classification and perspective," Information Sciences, vol. 235, no. 0, pp. 3-35, 2013.
[38] T. Yamamoto, K. Takao and T. Yamada, "Design of a Data-Driven PID Controller," IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 29-39, 2009.
[39] M.C. Campi, A. Lecchini and S.M. Savaresi, "Virtual reference feedback tuning: a direct method for the design of feedback controllers," Automatica, vol. 38, no. 8, pp. 1337-1346, 2002.
[40] Simone Formentin and Alireza Karimi, "Enhancing statistical performance of data-driven controller tuning via $\mathcal{L}_2$-regularization," Automatica, vol. 50, no. 5, pp. 1514-1520, 2014.
[41] Zhongsheng Hou and Shangtai Jin, "Data-driven model-free adaptive control for a class of MIMO nonlinear discrete-time systems," IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, vol. 22, no. 12, pp. 2073-2188, 2011.
[42] Zhongsheng Hou and Yuanming Zhu, "Controller-Dynamic-Linearization-Based Model Free Adaptive Control for Discrete-Time Nonlinear Systems," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 2301-2309, 2013.
[43] Leandro dos Santos Coelho, Marcelo Wicthoff Pessôa, Rodrigo Rodrigues Sumar and Antonio Augusto Rodrigues Coelho, "Model-free adaptive control design using evolutionary-neural compensator," Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 499-508, 2010.
[44] M. G. Safonov and Tung-Ching Tsao, "The unfalsified control concept and learning," IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 843-847, 1997.
[45] M. Stefanovic and M. G. Safonov, "Safe Adaptive Switching Control: Stability and Convergence," IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 53, no. 9, pp. 2012-2021, 2008.
[46] Jeroen van Helvoort, Bram de Jager and Maarten Steinbuch, "Direct data-driven recursive controller unfalsification with analytic update," Automatica, vol. 43, no. 12, pp. 2034-2046, 2007.
[47] J. van Helvoort, B. de Jager and M. Steinbuch, "Sufficient Conditions for Data-driven Stability of Ellipsoidal Unfalsified Control," 2006 45th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 453-458, 2006.
[48] Simone Baldi, Giorgio Battistelli, Edoardo Mosca and Pietro Tesi, "Multi-model unfalsified adaptive switching supervisory control," Automatica, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 249-259, 2010.
[49] Edy Bertolissi, Mauro Birattari, Gianluca Bontempi, Antoine Duchâteau and Hugues Bersini, "Data-driven techniques for direct adaptive control: the lazy and the fuzzy approaches," Fuzzy Sets and Systems, vol. 128, no. 1, pp. 3-14, 2002.
[50] Ioannis Kanellakopoulos, Petar V. Kokotovic and Richard Marino, "Robust adaptive nonlinear control under extended matching conditions," DTIC Document, 1990.
[51] Wassim M. Haddad and Vijaysekhar Chellaboina, Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Control: A Lyapunov-Based Approach, Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2008.
[52] V.Chellaboina and W.M. Haddad, "A unification between partial stability and stability theory for time-varying systems," IEEE Control Systems Magazine, vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 66-75, 2002.
[53] Wassim M Haddad, VijaySekhar Chellaboina and Qing Hui, Nonnegative and compartmental dynamical systems, Princeton University Press, 2010.